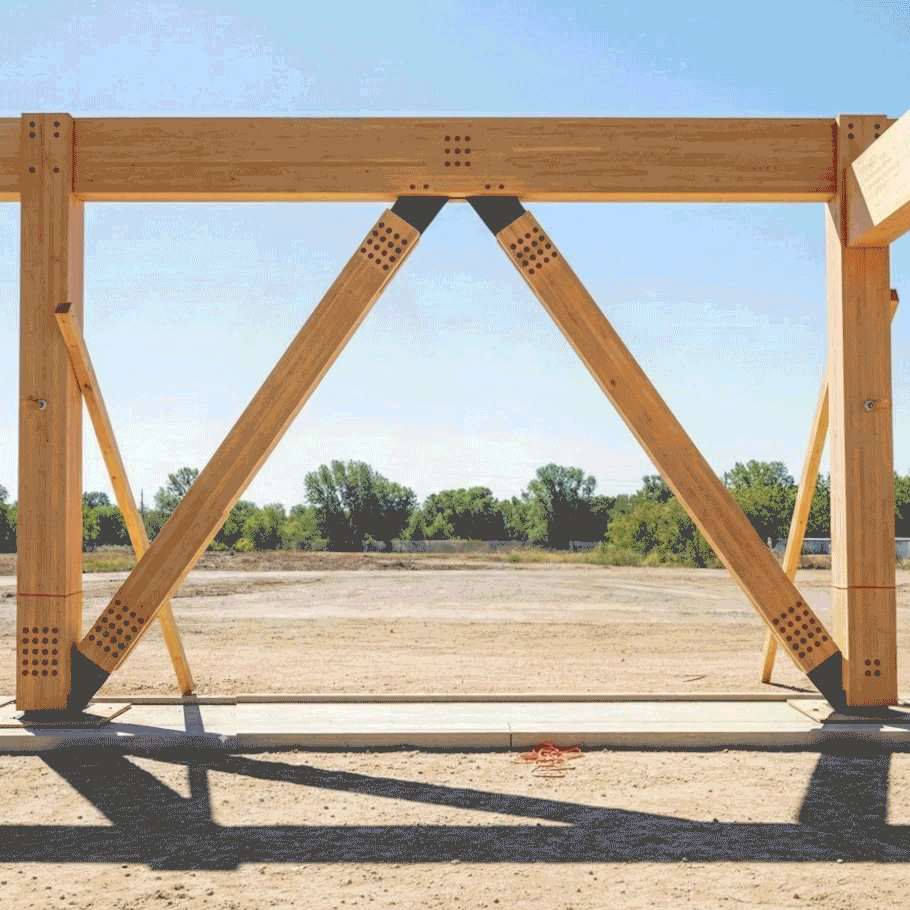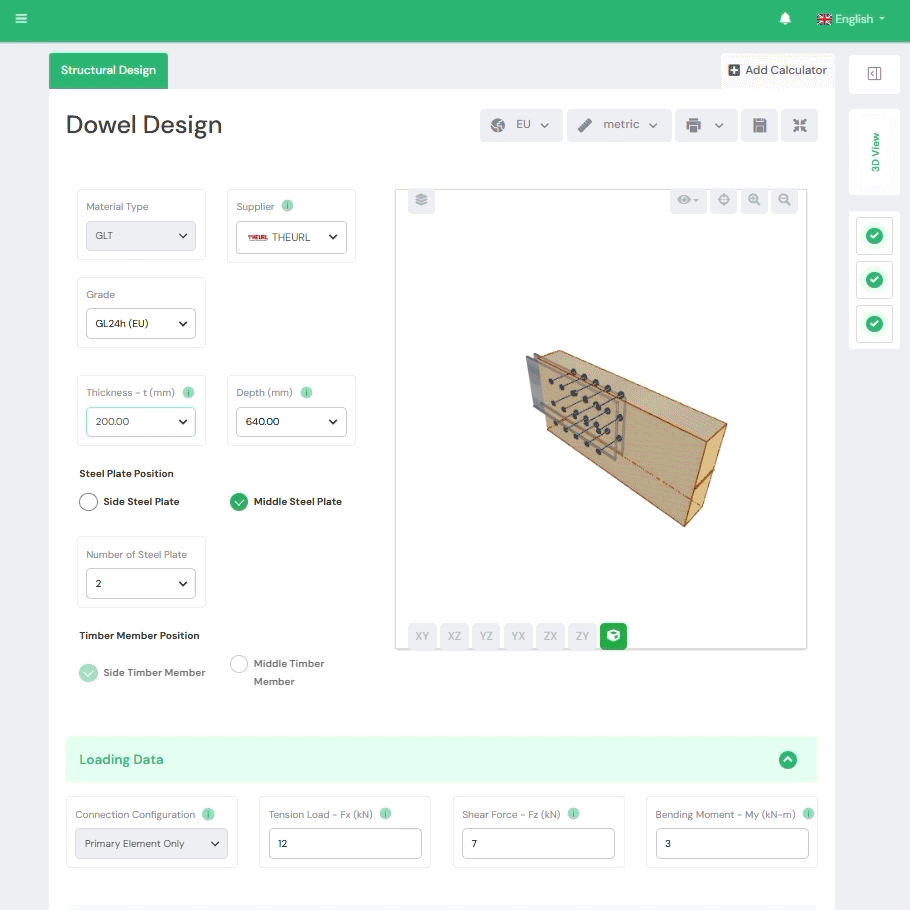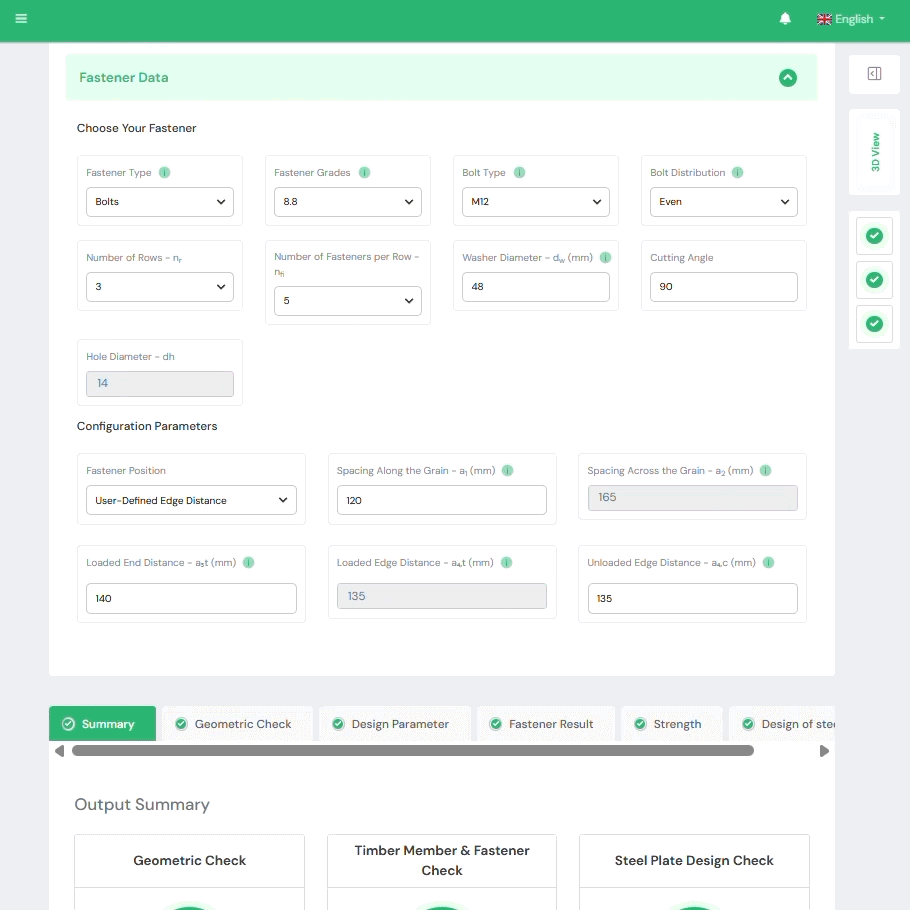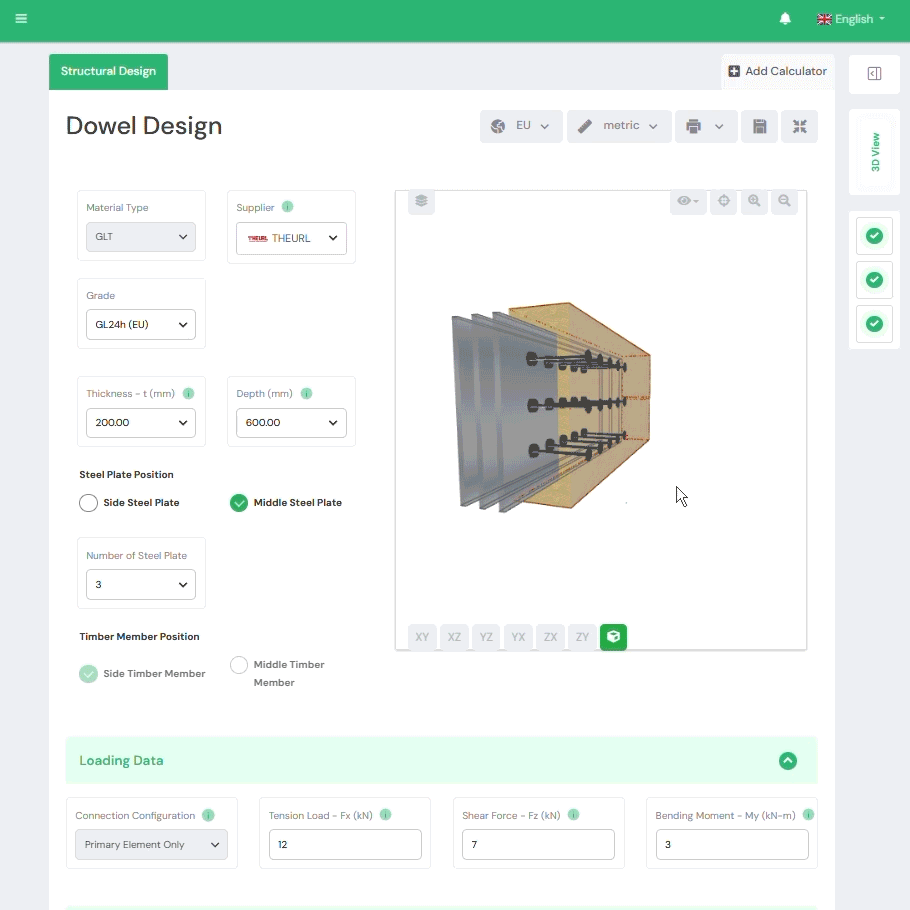
1. Yield Limit Theory (Automated)
CSA O86 requires checking multiple yield modes to find the “Unit Lateral Strength” ($n_u$).
Our calculator runs the full matrix:
- Mode a, b: Wood embedment failure (Main or Side member).
- Mode d: Fastener yielding with wood crushing.
- Mode e, f, g: Double curvature yielding (Plastic hinge formation).
- Feature: The tool identifies the governing mode. If it’s a ductile mode (steel yield), it allows for a more efficient design than brittle wood failure.
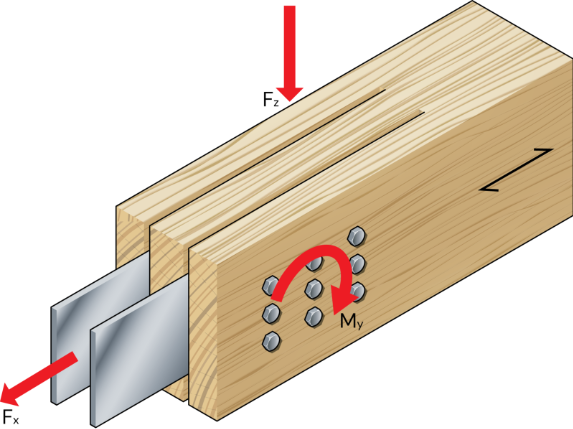
2. Combined Actions (Moment + Shear)
Standard CSA tables don’t tell you how to handle a moment-resisting knee connection.
Our module uses a Rational Analysis (Elastic Method). It resolves the applied Moment, Shear, and Axial forces into a resultant vector for every bolt. It then checks this resultant against the bolt’s capacity at that specific angle to grain ($N_{r,\theta}$), ensuring the “corner bolts” don’t fail.
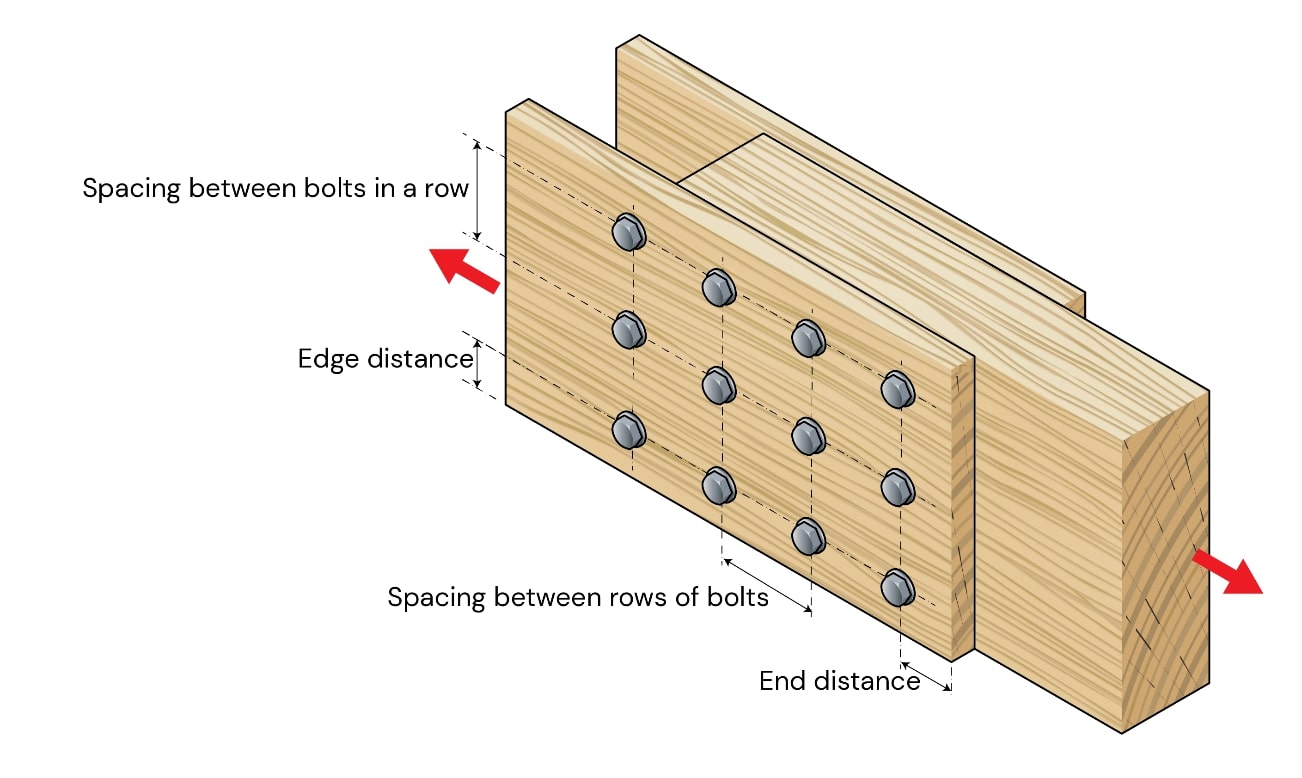
3. The Group Effect ($J_G$)
In a long row of bolts, the load is not shared equally.
The calculator calculates the Group Effect Factor ($J_G$) based on the number of fasteners per row, the stiffness of the members, and the ductility of the connection. This prevents the dangerous overestimation of capacity in large tension splices.